# Architecture
Effective software architecture patterns are essential for developing complex and scalable web applications. They are fundamental for ensuring the scalability, maintainability, and efficiency of modern software solutions.
In this guide, we explore various architecture patterns, from modular component-oriented approaches to contemporary architectures based on micro frontends, microservices, and Domain-Driven Design (DDD). We will analyze the principles, advantages, disadvantages, ideal use scenarios, and the implementation of each pattern on the Modyo platform.
This guide aims to provide a solid reference for architects and developers seeking to build robust, scalable, and future-proof applications by leveraging these architectural patterns.
High-Level Approach
This guide contains high-level patterns and is designed for software architects and technical leaders.
For a more specific review of programming patterns, we recommend the book “Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software” (opens new window) by Erich Gamma, Ralph Johnson, Richard Helm, and John Vlissides.
# Reference Architecture
Micro frontends are high-level user experience components orchestrated by the Modyo platform. Micro frontends run directly in the end user's browser and interact with microservices via APIs. Each micro frontend and microservice is designed to represent a specific business functionality and is developed, tested, and deployed independently.
The following figure illustrates the Modyo reference architecture, where micro frontends are deployed within the Modyo Platform, and microservices are deployed in a separate infrastructure, exposing their functionality via APIs.
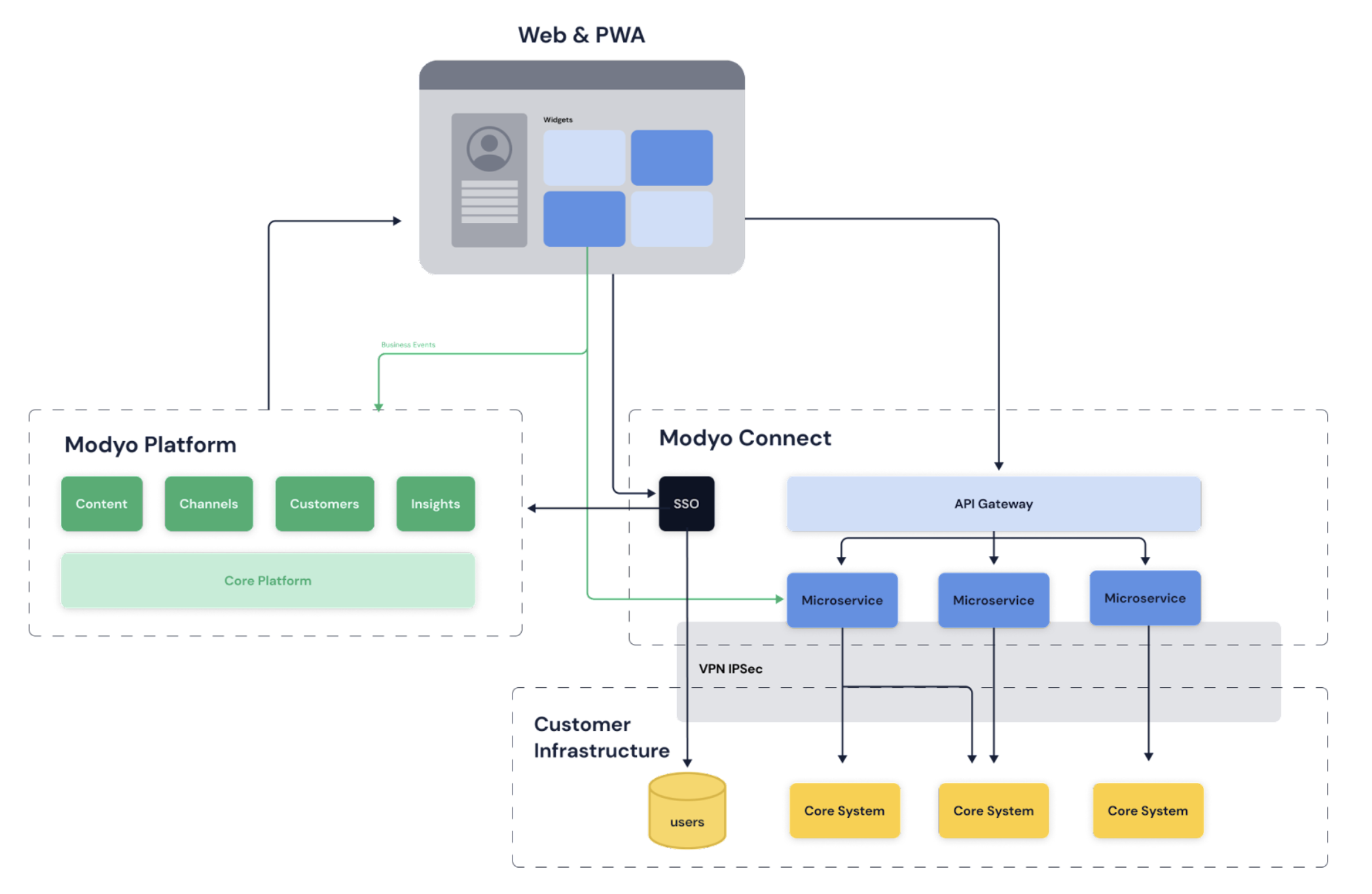
This architecture offers key advantages over a monolithic approach, enabling each component to be updated and scaled independently without affecting the rest of the system. This results in greater modularity, flexibility, maintainability, and scalability.
Furthermore, this decoupled architecture fosters greater independence among development teams. Each team can focus on their specific service or component without worrying about the rest of the system, which facilitates collaboration and streamlines the development process.
To model micro frontends and microservices from a business perspective, Modyo recommends utilizing the Domain-Driven Design (DDD) methodology.
# Modyo Connect
Modyo's reference architecture completely decouples the frontend from the backend by establishing a delimited context for API communication. While the frontend is fully managed by the platform, the backend requires a separate implementation. This implementation can leverage existing APIs or the Modyo Connect service.
Modyo Connect is an infrastructure service managed as a platform-as-a-service (PaaS). This service is managed by Modyo and deployed in a secure environment within the Modyo business cloud.
More information
For more information about Modyo Connect and its managed infrastructure components, see the official documentation.
# Architectural Patterns
Architectural patterns are proven and recommended solutions to common problems in software design and development. These patterns establish a structure and a set of rules for organizing and relating system components, which facilitates software development, maintainability, and scalability.
By utilizing architectural patterns, developers can leverage established best practices and adopt a structured approach to building high-quality applications. These patterns address concerns such as responsibility distribution, modularity, code reuse, and data management, among other essential aspects of software development. By following these patterns, development teams can create robust, flexible, and easy-to-maintain systems.
